SMD Components: A Look at Different Types and How to Identify Them
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole Technology (THT) are two common types of technology used with printed circuit boards (PCBs). Professionals in the industry must understand the distinctions and benefits of these components. This article provides a comprehensive overview of Surface Mount Device (SMD) and THT components, highlighting their shared characteristics, differences, and the advantages of using electronic components in PCBs.
Table of Contents
- Surface Mount Technology and Surface Mount Device
- Unveiling the distinction: SMD vs. THT components in electronic circuits
- Exploring the versatility of SMD components: A comprehensive guide to common types in electronic circuits
- Quality Control with Automated Optical Inspection
- Navigating the world of SMD components: Expert guidance for successful electronic device development
Surface Mount Technology and Surface Mount Device
SMT and SMD are related terms in electronics, especially in the manufacturing and assembly processes.
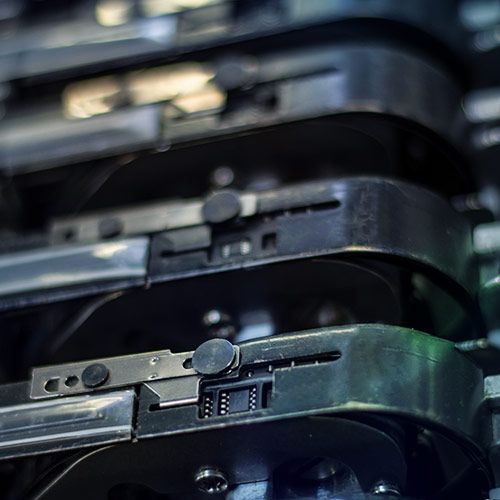
SMT is a process technology and methodology used to mount electronic components that are mounted on the surface of a PCB. This includes designing the PCB, adjusting the solder paste application, component placement (pick and place), reflow soldering and automatic optical control (AOI). SMT enables the use of various surface-mountable components, designed specifically to be directly mounted, including CHIP, MELF, QFN (Quad Flat No Leads), QFPs (Quad Flat Packages), SOICs (Small Outline Integrated Circuits) and BGA (Ball Grid Array).
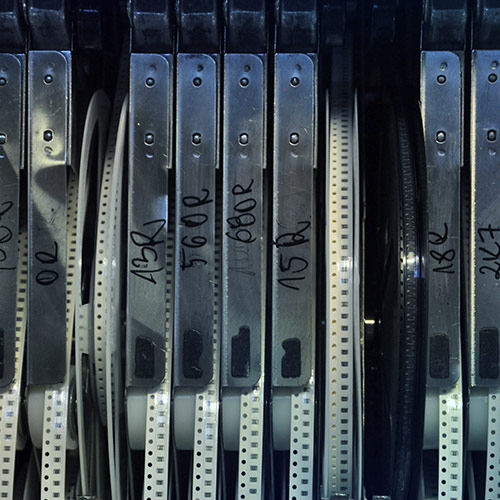
SMD components differ from THT components, as they concern only those mounted directly onto the PCB surface. These components have soldering pads, terminals, or balls on their lower surface, facilitating their surface mounting onto the PCB. SMD components come in a wide range of types and functionalities. From the typical passive chip resistors, chip capacitors, through semiconductor diodes, LED diodes, transistors, and various very large-scale integration components (IC).
SMT is a broad term that encompasses the entire surface-mount assembly process, while SMD refers specifically to those components mounted using the SMT process. Understanding this distinction enables effective communication and collaboration with professionals in the industry, to ensure the successful integration of these advanced technologies into electronic designs.
Unveiling the distinction: SMD vs. THT components in electronic circuits
SMD and THT components serve similar electrical functions in electronic circuits, but differ in size and miniaturization possibilities.
THT components are installed on the PCB by inserting their leads into holes on the board and soldering them on the opposite side (Soldering Wave). They offer a sturdy mechanical connection and are often used for components requiring higher power. THT technology is known for its ease of manual assembly and easier potential service possibilities.
SMD components are mounted directly onto the surface of the PCB, eliminating the need for drilled holes. They are smaller in size compared to THT components, allowing increased miniaturization and more flexible designs. Increasing the functionality of devices and their simultaneous miniaturization (in Smartphones or Tablets) is possible thanks to SMD components. These components can also be mounted on flex or rigid-flex boards, providing extra-additional design possibilities.
Automated assembly of surface mount components enables cost optimization and process efficiency, ensuring fast, precise, repeatable, and high-quality production. SMT has partially supplanted and has largely replaced THT in the electronics industry due to the advantages in size, flexibility, and automation.
Exploring the versatility of SMD Components: A comprehensive guide to common types in electronic circuits
SMD components offer a wide range of options, each serving specific functions in electronic circuits. Here are some of the common types:
- Chip resistor: small surface-mount components used to provide specific resistance values, labeled with numerical codes for easy identification.
- Network resistor: interconnected resistors in a ladder-like configuration, allowing precise resistance values to be achieved by combining multiple resistors in a single package.
- Ceramic capacitors: compact capacitors available in nanofarads or picofarads, commonly used for tasks such as noise filtering and decoupling.
- Electrolytic capacitors: aluminum construction and polarity characterize these capacitors, denoted in microfarads, often employed for their high capacitance values.
- Tantalum capacitors: polarized capacitors offering significant capacitance values while maintaining a compact size, similar to electrolytic capacitors.
- SMD inductors (coils): passive surface-mount components in various chip sizes, crucial for such applications as filtering and energy storage in electronic circuits.
- Transformers: essential components for voltage transformation, enabling the conversion of electrical energy between different voltage levels.
- IC: various semiconductor devices, including diodes and LEDs, packaged in formats like SOT (Small Outline Transistor), SOP (Small Outline Package), MELF (Metal Electrode Face), etc., facilitating their integration into electronic systems.
- Semiconductor IC packages: packaged versions of integrated circuits, such as BGA, FBGA, LCCC, PPGA, QFP, etc, offering different configurations and pin layouts for efficient and reliable mounting on circuit boards.
- Quartz resonators or oscillators: employed primarily in clock circuits, these components come with 2 or 4 leads and provide precise and stable frequency references for timing applications in electronic systems.
Quality Control with Automated Optical Inspection
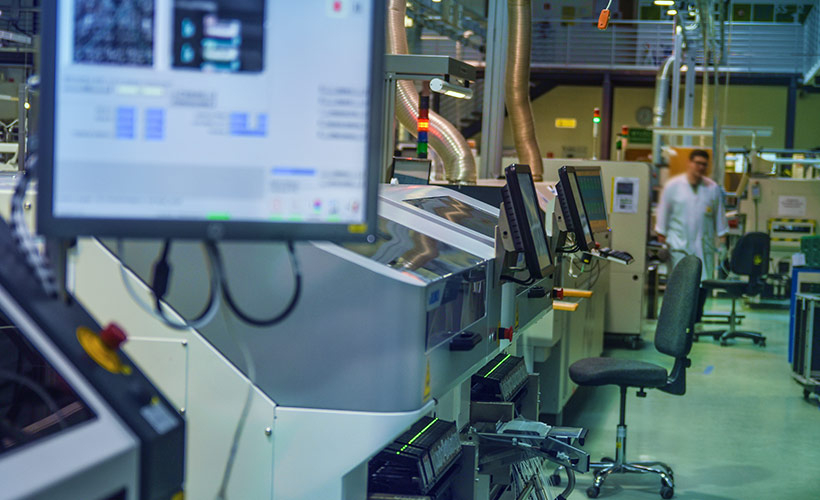
Ensuring the quality and reliability of electronic equipment is paramount in today's demanding market. At VECTOR BLUE HUB, we utilize AOI 3D technology as part of our comprehensive quality control process.
AOI systems employ high-resolution cameras supported by blue laser and advanced algorithms to inspect the assembled PCBs with precision and efficiency. Precise reconstruction of the soldering shape (3D) makes it possible to obtain products free of any defects. By analyzing such aspects as component placement, solder joints, polarity, and correct orientation, AOI helps identify potential defects and anomalies that may affect the functionality and reliability of the final product.
With AOI 3D, we perform thorough inspections of entire circuits in a short period, significantly enhancing the speed and accuracy of our quality control procedures. This advanced technology enables the detection of defects that may go unnoticed through manual inspections, ensuring that only the highest quality products leave our manufacturing facility.
By incorporating AOI 3D into our quality control process, we provide you with confidence and peace of mind, knowing that your electronic equipment meets the strictest standards of performance and reliability.

Navigating the world of SMD components: Expert guidance for successful electronic device development
At VECTOR BLUE HUB, we understand the complexities and challenges of navigating the world of SMD and THT components in electronic circuit design and assembly. Our team of experts offers you a range of invaluable services to ensure your success.
From design and component selection to PCB layout and seamless assembly, we guide you every step of the way. We prioritize precision, repeatability, and the highest quality standards, leveraging state-of-the-art automation techniques to optimize cost-efficiency and streamline manufacturing processes.
Our commitment extends beyond the assembly line. Thorough quality control measures, including AOI 3D, verify the integrity and functionality of your finished components. Trust us to deliver reliable, high-performance electronic solutions that meet your exact specifications.
Partner with VECTOR BLUE HUB to access industry knowledge, personalized support, and tailored solutions that can propel you towards success. Build a long-term relationship with us, and let us help you navigate the complexities of SMD and THT components, elevating your electronic designs with precision and excellence.
Contact us today.