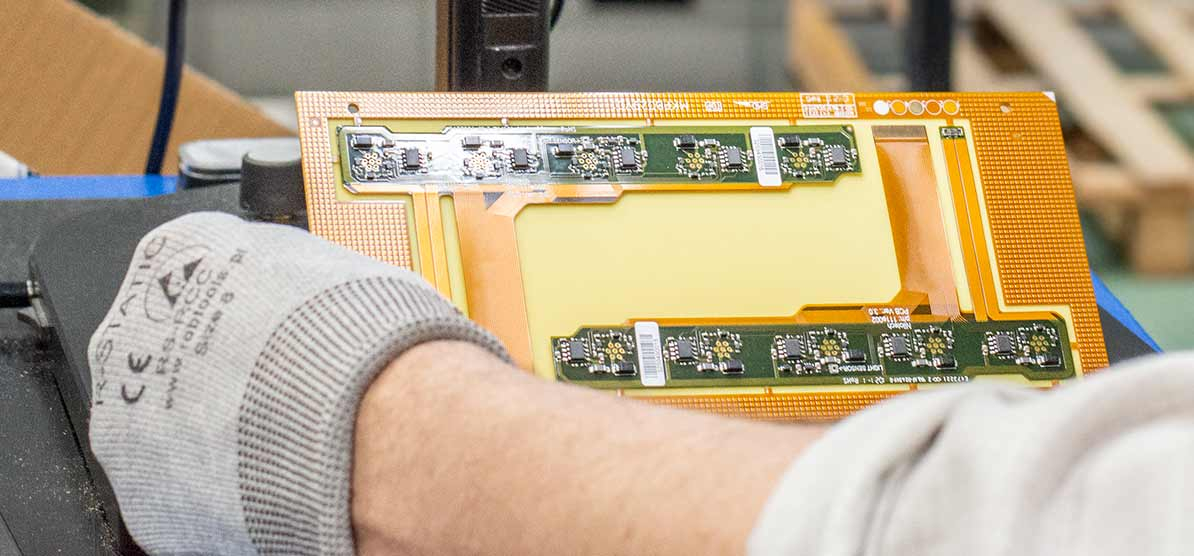
Flexible PCB assembly (PCBA) for medical device
The Industry 4.0 revolution redefines the way people, machines, and companies connect worldwide. Our awareness grows simultaneously with our desire to harness the Internet of Things (IoT) to facilitate data collection, such as by medical devices, wearables running on Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) or smart devices using Radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags. Here a challenge arises for electronic manufacturing companies, as they need to replace the traditional circuit board with a flexible printed one (PCB).
Flex circuits are now in high demand, and it seems that this trend will continue to grow. Why are flexible PCBs so desirable and indispensable for the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)? In the evolution of electronics, flexible PCBs have enabled many medical and laboratory devices to become smaller, smarter and lighter. Bearing the exact same request came one of our customers, specializing in quality control instrumentation for specific laboratories. What was the recipe for the fast and successful completion of a flexible printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) prototype for medical laboratory use? Read our case study to find out!
What is a flexible PCB?
The printed circuit board is the foundation for the construction of electronic devices. But the more complex the project becomes, the greater the difficulty in achieving the ideal PCB for an electronic product. Let's then take a closer look at the main definitions of a PCB.
Initially, PCB manufacturers made simple circuits as single or no more than two-layer PCBs. Since then, the production method has evolved until now it allows the creation of complex, multilayer printed circuit boards and rigid-flexible PCBs.
A flexible PCB begins by drawing conductive paths onto a dielectric substrate. Each board contains flexible laminates made of special materials to ensure the flexibility of the finished board. These types of laminate primarily rely on a thin polyimide (PI) film as a substrate to protect the board from high temperatures. The resulting flexible printed circuits can easily fit into any shape of electronic device without any loss of its properties.
Depending on the number of layers to be bent, we can distinguish several types of flex circuit in PCBA:
- Single-sided flex – min. bend radius: 3-6 times circuit thickness,
- Double-sided flex - min. bend radius: 7-10 times circuit thickness,
- Multilayer flex - min. bend radius: 10-15 times circuit thickness (or more),
- Dynamic flex applications (single-sided) - min. bend radius: 20-40 times circuit thickness.
Global trends in PCB manufacture
According to the fresh market report published by Global Industry Analysts Inc. (GIA), the global Flexible Printed Circuit Boards Market may reach $19.5 billion by 2026. As the study implies, a significant advantage of a flexible PCB over a conventional rigid PCB is that the latter design cannot take a particular shape at the time of manufacture that allows it to flex during use in a medical device, for example.
On the other hand, it's projected that the market for the most common type of flexible circuit, the single-sided flex PCB, is going to reach $3.1 billion by 2026.
All of the above lead to the conclusion that boards designed to fit inside a designated system will, step by step, conquer the market of smart electronic devices.
Source: PR Newswire
Flexible circuits can bring many advantages, such as:
- smaller dimensions, especially thickness,
- ower weight, compared to traditional PCBs,
- ease of adapting the board to the housing shape, allowing agile assembly.
Printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) prototyping for a medical device – the customer requirements
Our customer specialises in quality control instrumentation for specialised laboratories. Its product guides the user through the control and calibration of critical equipment in a specific laboratory environment. As a result, the medical product can control and calibrate incubators, IVF workstations, warming systems, etc., with no need for other third-party instruments. The product itself is compact, so the technology inside should be as well. That's why for this PCBA process, rigid-flex was so essential.
The combination of flexible circuits with a rigid PCB improves connectivity between other circuit board and electronic components. The traditional SMT assembly with rigid PCB wouldn't be successful for this medical product for many reasons: it was time-consuming due to producing several boards, soldering electrical circuit boards, and mounting them. Flex circuits provide connectivity in dynamic flex applications where the flexible circuit needs to flex continuously over the life of the device, so choosing this specific board was more advantageous for our customer.
Here the story begins - the design of a flexible circuit
The flexible PCB modelling and prototyping require an agile approach and various skills. Firstly, the components cannot be placed near the bending material due to PCB's elastic nature. Also, the board can tear if flexed beyond its capability when mounting in the device. What's more, classic PCB design programs show a flat image, so the final result remains with the PCB designer and PCBA engineer and their close cooperation.
The team had to find the right answer to challenging questions in the range of Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA) to complete the process successfully. How do the elements bend, and how do they fit into the medical device housing? Which areas need to be stiffened to prepare PCB for manufacturing? Combining the team’s spatial imagination and cross-sectional knowledge of the entire PCBA process results in modelling a PCB well prepared for production.
The challenge - generating flexible circuit boards thermal profile.
A PCBA engineer is vital for assemblies, from concept to high volume manufacturing. In this project, it was crucial to set the perfect thermal profile dedicated to the board because the flex PCB has a fragile plate that quickly absorbs heat. With a standard thermal profile for the rigid printed circuit boards (FR4), the components overheat, which results in low reliability of the device.
We passed the test plate with the thermocouples and placed them several times through the reflow oven to obtain the necessary temperature measurements in critical places during the entire soldering process. Each heating zone in the furnace has a specific time and temperature we couldn't exceed. The idea was to fit within both the solder paste process window and the component process window in order to find the right balance to meet the requirements of each. These actions ensure a well-soldered paste and stable mechanical connections. Because the elements are not overheated, we achieve the famous five-nines - high availability of the services.
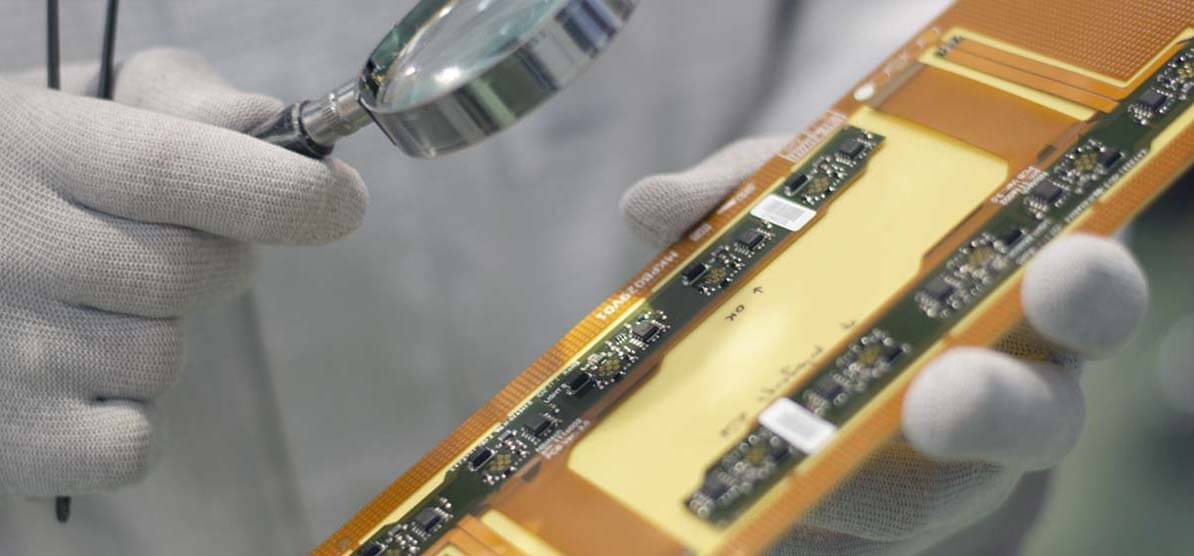
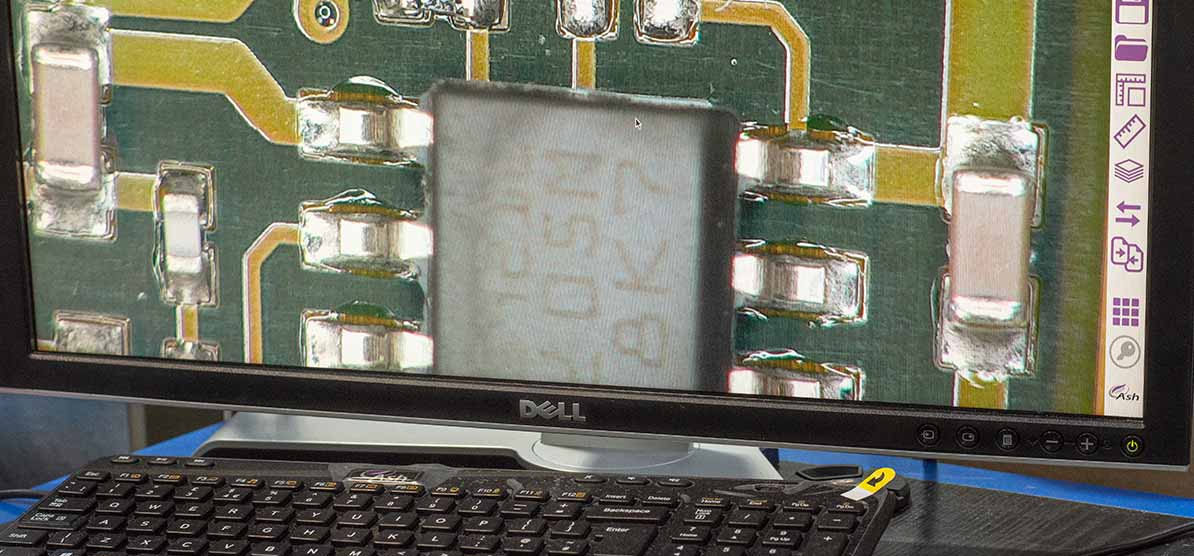
Flex circuits quality control
At the end of the process, we could lean on our Quality Assurance team that put all their effort into conducting tests, delivering proper documents and designing the process so that the cost-quality balance falls into the optimal point.
A key element in PCBA - the experienced printed circuit broker
Having a qualified partner in PCBA manufacturing that supports our product development process was essential to complete this project. To ensure a guarantee of high-quality electronic components, we choose Elmatica, which has a strong background in the medical industry, delivering their first Flex-Rigid board in 1992! Impressive, right?
Indeed, from the PCB manufacturer's side, completing this project required a ... flexible approach. We spent many hours seeking the best solution for this particular project because we couldn't easily pass the flexible circuits through the production line. So, we took advantage of the know-how in assembling rigid PCB. As a result, we used the traditional circuit board as a safeguard and bound the flex PCB on it using the tabs. The Elmatica's expertise and the agility of our PCBA engineers sped up the whole process and helped us achieve a satisfying result.
Flexible PCBA of medical device - the result
In bridging the flexible PCB and sublimate hardware gap, the combined VECTOR BLUE HUB and Elmatica solution supports our customer in delivering lab instruments that can perform most quality controls in the IVF stem cell laboratory with just one reference instrument.
In VECTOR BLUE HUB, we hold knowledge and competence which will answer many PCBA challenges in medical sector, industrial IoT and communication technologies. Sign up for a free consultation and let’s discuss your next pro